The disease caused by a violation of the structure of the vascular walls, their thinning, with pronounced stagnant blood flow processes, is called varicose veins. The disease often affects the lower extremities, although it can be localized in the rest of the body. According to the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision of ICD 10, varicose veins are assigned code 183, which includes four headings describing various manifestations of the disease.
How did varicose veins appear?
The first mentions of varicose veins were found in ancient Greek papyri. History and confirmed scientific facts say that varicose veins of the lower extremities were found in the found Egyptian mummy - it can be argued that the disease accompanies humanity throughout its existence.
Outstanding doctors - Avicenna, Hippocrates, Galen tried to treat varicose veins of the lower extremities. In the nineteenth century, painful and traumatic methods of treatment were used, which consisted of dissecting the tissues of the thigh and lower leg to damage the saphenous veins, followed by bandaging. It was understood that in this way it is possible to prevent stagnant blood flow processes and varicose veins will be eliminated. However, the methods left terrible, extensive scars on the patients' bodies, and contributed to damage to nerves, arteries and disruption of lymph flow.
A little later, the history of the treatment of varicose veins received a positive breakthrough - in 1908, for the first time, a metal probe was used as a means of minimally invasive effect on the walls of blood vessels. The discovery of radiography made it possible to carry out more accurate and efficient surgical operations to eliminate varicose veins. Now, when the correct diagnosis and treatment of the disease is needed, duplex and triplex scanning, powerful medications, laser therapy and sclerotherapy are used. Surgical intervention is used only in cases where varicose veins cannot be eliminated sparingly.
The main causes of the disease
Varicose veins represent a great danger, the pathology has become "younger" - before, mostly elderly people suffered, now varicose veins are diagnosed in young patients, extremely rarely in children.
Causes of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Overweight, overweight, obesity.
- Sedentary inactive lifestyle.
- Improper diet, poor blood quality.
- Concomitant disease of the cardiovascular system.
- Professional activity.
- Prolonged standing, heavy physical exertion.
- Pregnancy and hormonal changes.
- Individual features of the structure of the vascular system.
- Pathological congenital diseases.
- Wearing shoes with heels, tight clothing.
- Thermal treatments.
Any of the above reasons can provoke the development of varicose veins, the consequences are dangerous, including death.
The structure of the venous vessels
To understand what causes the varicose veins of the lower extremities, you need to have an idea of the structure of the vascular system and the mechanism of its work. It represents the totality of the main (deep and superficial) and connecting perforating (communicating) veins.
The small superficial vein begins in the area of the foot, stretches along the back of the lower leg, branches under the knee into two branches, connects with the popliteal vein and the deep femoral vein.
A large superficial saphenous vein forms in the ankle region, runs along the surface of the lower leg and knee joint, and connects to the femoral vein. Deep veins are located along the branches of the arteries, and the whole venous system is connected by perforating vessels.
With normal blood flow, oxygenated blood flows directly to the heart, and special venous valves prevent backflow. Varicose veins of the lower extremities implies strong pressure, the diameter of the venous lumen increases significantly, the valves do not cope with the task, reflux occurs - reverse blood flow. Improper blood circulation provokes excessive expansion (stretching) of the vascular walls, their thinning, venous obstruction and blood stasis. As a result - bloating, swelling of the veins, the formation of nodes.
Symptoms and clinical presentation
Varicose veins are able to progress for a long time in a latent form, then the signs appear:
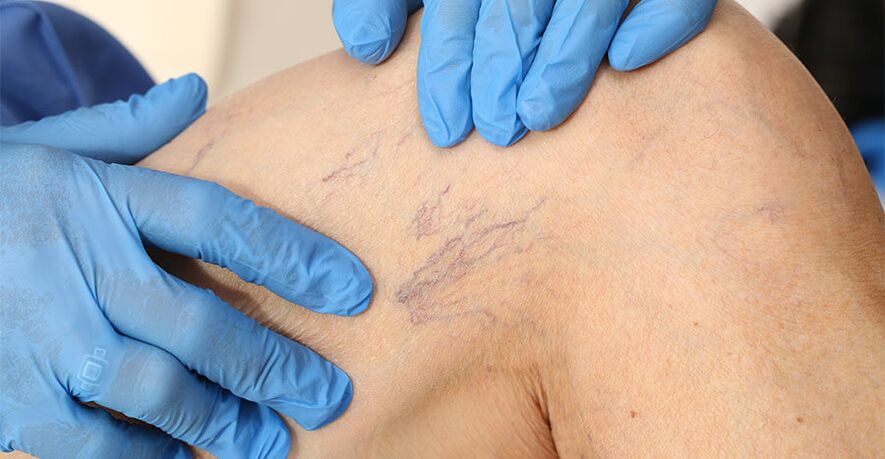
- The formation of spider veins is a mesh accumulation of dilated small veins.
- Well-defined pattern of congested veins protruding under the skin.
- The formation of places of compaction of blood vessels - varicose veins in the form of well-distinguishable tubercles on the legs.
- A change in the normal color of the skin, cyanosis, blackness appears, the upper layer (dermis) acquires a loose structure.
- Feeling of pain, heaviness, distention and fatigue of the legs, decreased mobility, difficulty walking.
- With varicose veins of the lower extremities, the formation of swelling of soft tissues is possible.
Ignoring timely treatment leads to serious and dangerous consequences, when a person can be cured only by immediate surgical intervention.
Disease classification
Varicose veins according to ICD 10 are classified into a disease with an ulcer, with inflammation, with an ulcer and inflammation, when these signs are absent. According to the international classification of chronic venous diseases, created in 1994, varicose veins are classified into:
- Intradermal, segmental. No pathological venous discharge is observed.
- Segmental with reverse blood flow, occurs through the superficial and perforating veins.
- Distributed with reverse blood flow through superficial and perforating veins.
- Varicose veins with reverse blood flow through the deep veins.
It is customary to divide the disease according to additional signs of the clinical picture:
- On examination or palpation, there are no symptoms.
- The reticular veins are expressed.
- There are varicose veins.
- There is swelling of the soft tissues.
- Violation of the normal skin color.
- Revealed lipodermatosclerosis.
- There is a healed ulcer.
- An active ulcer was revealed.
Symptoms are absent or are subjective (patient's feelings). Additionally, varicose veins are classified for reasons: congenital, primary, secondary, with an unknown factor that provoked the development of the disease.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
The predominant way to detect varicose veins is visual examination and palpation of the patient. In order to carefully determine the severity of the disease and choose the correct treatment, when the medical history is studied and palpation is applied, the phlebologist prescribes:
- A complete blood count is the main standard for determining the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin levels. According to blood clotting, conclusions are drawn about the degree of development of the disease and the predisposition to thrombosis.
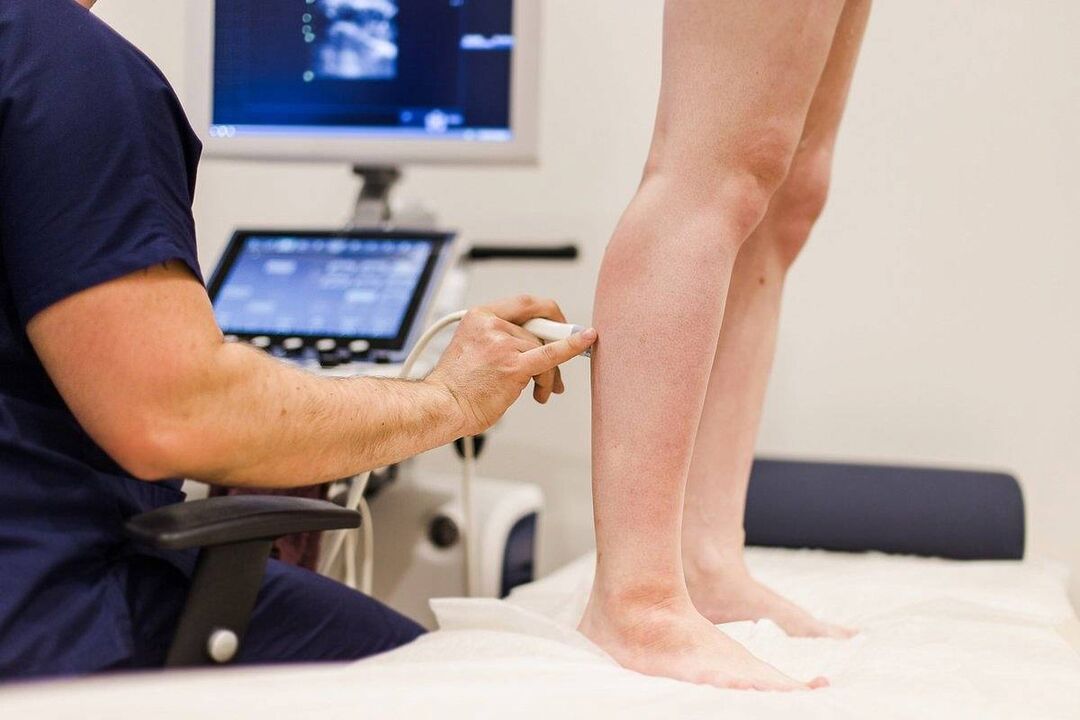
- Doppler ultrasound. The method consists in ultrasound diagnostics of the speed and direction of blood particles. This allows you to establish in which direction the blood flow is carried out, whether it has sufficient speed.
- Ultrasonic agnioscanning. It is used for visual examination of the vascular walls, their structure, direction and speed of blood flow in real time on the monitor of the ultrasound machine.
- Plethysmography. Diagnostics is based on detecting the electrical resistance of the leg tissues. With proper circulation, the parameter should indicate the normal standard.
- Rheovasographic diagnostics. Based on the determination of the index of tissue blood filling. The rheographic index helps to determine the stage of varicose veins - compensation, subcompensation or decompensation.
The history of the disease and its study, obtaining comprehensive diagnostic data, allow the doctor to choose the method of treatment.
Conservative drug therapy
This method of treatment involves the appointment of special drugs that have a positive effect on the course of the disease. Conservative treatment of varicose veins is effective in the initial stages, is used as an additional method of influence in the formation of nodes, ulcers, eczema.
The main groups of drugs prescribed are:
- Phlebotonics and phleboprotectors. Venotonic drugs are the standard, implying conservative treatment. Promote the restoration of the structure of the vascular walls, strengthen and tone the blood vessels.
- Means for effective blood thinning. They help to improve the quality composition, blood flows faster through the veins, reduce the risk of blood clots, restore normal blood circulation, and relieve pain.
- NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs). Eliminate pain, prevent cramps, effectively relieve inflammation and swelling.
Conservative treatment helps with timely referral to a phlebologist, at the initial stage it is possible to influence the blood composition and the state of the vascular walls. With complex forms of the disease, drastic measures are required.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is recognized as a gentle and least traumatic method when varicose veins of the legs require treatment classified according to ICD 10 code 183. The idea of the method is to use a laser beam that actively affects the vascular walls and promotes their adhesion. An LED connected to a laser device is inserted into the vein by piercing the skin. The beam is selective and has no effect on adjacent healthy tissue. Significant advantages of laser therapy in the treatment of varicose veins:
- Fast positive effect.
- Absence of pain and injury.
- Stable result, long-term remission.
- Restoration of normal blood circulation.
Contraindications to use will be thick or too thinned vessel walls, large venous lumens, pregnancy, oncology and other serious concomitant diseases.
Sclerotherapy for varicose veins
The method is based on the introduction into the vessels affected by varicose veins of special liquid or foam preparations - sclerosants. They replace endothelial cells with fibrous tissues. To perform sclerotherapy, needles, syringes and sclerosants are used.
The treatment technique consists of the following steps:
- piercing of a pathological vein;
- pumping out (removing) all blood from the vessel;
- administration of a sclerosant preparation;
- the imposition of an appropriate bandage or knitted compression.
This method gives a lasting result. The procedure is painless, fusion of vascular tissues with varicose veins is an alternative to surgery.
Performing an operation
The most painful and traumatic way to treat varicose veins is considered to be surgery. Indications for carrying out will be extensive vascular lesions, the presence of varicose veins, dangerous consequences of the disease, for example, acute thrombophlebitis.
Phlebectomy is performed under local anesthesia, the pathological vein is ligated, the required number of incisions are made to remove it, and removed. The operation is recognized as an effective method of treatment, shows the result in eighty percent of cases. But phlebectomy has a number of side effects: wound complications, trauma to the lymph nodes, in extreme cases, with damage to deep nerves, immobilization and disability can occur.
In order to prevent dangerous complications of varicose veins, which are manifested by: nodes, ulcers, bleeding, phlebothrombosis, pulmonary embolism and other serious consequences, you should consult a doctor at the initial stage of varicose veins!























