Varicose veins of the lower extremities are a problem that overtakes more than 60% of the world's population. The term "varicose veins" from the Latin "varix" is interpreted as "expansion". Hence the definition of the pathological condition - the expansion of the lumen of the veins of the lower extremities and the pelvic organs, which significantly impairs blood flow in the vessels and, accordingly, worsens the general condition of the patient. In the material below, we will consider the causes of varicose veins, possible complications of the disease and the main ways of dealing with pathology.
Causes and risk factors: everyone is susceptible to this
Important:if varicose veins overtake young people under the age of 25, then here the gender distribution occurs 50: 50. That is, both boys and girls are equally ill. At a more mature age, women are more likely to have varicose veins due to pregnancies and age-related significant changes in hormonal levels.
If we consider varicose veins from the inside, then anatomically, the expansion of the lumen of the veins occurs due to a malfunction of the venous valves that regulate blood flow. Malfunctioning valves do not close fully with every heartbeat. As a result, blood coming from the heart in jerks moves to the lower extremities due to the force of gravity.
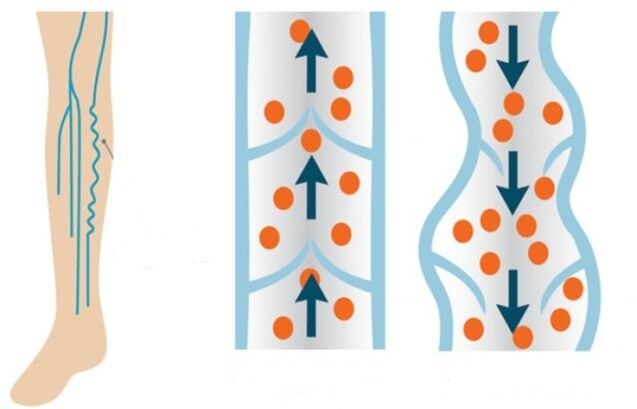
Normally, the valves should close and allow blood to flow to the legs in portions. But, unfortunately, the blood flow enters the legs more intensively, and in the opposite direction it moves less intensively due to the same poor functioning of the valve system. Veins of the legs overflowing with blood lose their elasticity and stretch over time.
The main predisposing factors for the development of a pathological state of blood vessels are:
- genetic component (the disease can be transmitted through the female or male line within the family);
- overweight;
- postponed pregnancies;
- passive lifestyle;
- excessive physical activity;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- hormonal disorders.
Male problems
If we consider the causes of varicose veins, depending on the gender of the patient, then in men and women they are somewhat different. More precisely, each of the representatives of different sexes is prone to certain habits, which sooner or later can provoke the pathology of the vessels of the lower extremities. So, for men, risk factors are:
- strength training with lifting weights from the squat position;
- overweight and obesity;
- unbalanced diet, which provokes frequent constipation;
- pathological processes of the kidneys (tumors of various etiologies);
- inguinal hernia;
- sedentary work;
- smoking and drinking alcohol.
Important:for men, not only the development of varicose veins of the lower extremities is characteristic, but also varicose veins of the spermatic cord. This pathology is called varicocele. Such a condition is inherited, that is, it is exclusively genetic in nature and is not prevented even by enhanced preventive measures. Only 2-4% of men suffer from varicocele. The cause of the pathology is the asymmetrical anatomical location and structure of the male genital organs.
Due to the fact that men suffer from false bashfulness or do not have time to visit a specialist at the very beginning of the disease, varicose veins are more difficult for them than for women.
Women's varicose veins have their own laws
For women, varicose veins are more "familiar" than for men. More than 80% of women suffer from vascular pathology of the legs. Moreover, the risk group includes the fairer sex who prefer this lifestyle or experience the following conditions:
- wearing tight high-heeled shoes;
- sedentary or standing work;
- hereditary predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy or with autoimmune diseases;
- wearing too tight underwear, jeans;
- smoking;
- low percentage of fruits and vegetables in the diet (constant diets and starvation);
- love of tanning (frequent visits to the solarium or stay in direct sunlight);
- sharp weight gain;
- low mobility.
Pregnancy is where the "dog is buried"
Even if the manifestations of varicose veins, the causes and treatment of which should be established and prescribed only by a phlebologist, are not initially observed in a woman, in 30% of cases it becomes obvious during pregnancy. Here, the main pitfall lies in the growing fetus and with it the uterus, which intensely squeeze the pelvic organs. As a result, blood circulation in the lower body is significantly impaired. The reverse flow of blood from the legs upwards is difficult. This effect on the deep veins of the legs leads to the fact that the vessels are actively stretched both in width and length.
In addition to the growth of the uterine organ and the pressure exerted on the vessels of the pelvic organs, varicose veins in pregnant women also develop under the influence of such factors:
- Increased blood clotting. Thus, nature insures a woman from large blood loss during childbirth. Thicker blood moves harder through the veins.
- An increase in the level of the hormone progesterone, which leads to relaxation of the muscles and blood vessels of the uterus, so that it can increase freely and without tone as the fetus grows. But at the same time, the walls of the remaining vessels also relax. Veins become less elastic, and thick blood even more stretches their walls already weakened by progesterone.
- Increase in blood pressure for better oxygen supply to the fetus. As a result, the body tries to quickly drive thick blood through the relaxed vessels. Its volume in the legs increases due to this.
- Low mobility of a pregnant woman with the growth of the tummy. This leads to stagnation of blood in the legs and pelvic organs.
Complications of varicose veins
If varicose veins are not treated and paid attention to, then over time, the patient may develop very serious complications that may require even a full-fledged surgical intervention. In the worst case, the patient may undergo amputation of the diseased limb. Below we will consider the most common and dangerous complications of varicose veins.
Chronic venous insufficiency
With the development of such a complication, an active failure of the venous valves occurs. Moreover, the pathological process is divided into four stages:
- Zero. The patient feels slight swelling and infrequent soreness in the legs after a hard day.
- First. On the surface of the skin, the venous network of the dilated vessels is visualized.
- Second. Swollen veins with blood clots and nodes in them are clearly visible. There is reddening of skin areas in places of inflamed veins, itching, sores.
- Third. Trophic ulcers form on the legs with inflamed veins.
Important:signs of chronic venous insufficiency are itching of the legs, soreness, burning sensation in a prolonged sitting position, swelling, night cramps.
Thrombophlebitis of superficial veins
In this case, the patient develops a tendency to form blood clots. Clots actively block the lumen of the veins, making it difficult for blood to flow. In most cases, blood clots and clots are localized in the vessels of the lower third of the thigh or upper third of the lower leg. The symptoms of venous thrombophlebitis are:
- redness of the skin of the legs in places of clot formation;
- pain in the legs;
- on palpation - induration in the veins.
Important:with thrombophlebitis, it is necessary to wear compression hosiery. The compression formula should be selected by a specialist - angiosurgeon or phlebologist.
Trophic ulcer
This complication manifests itself already in the later stages of venous insufficiency. First, the patient develops increased vascular permeability. A whitish seal with a varnish-like surface forms on the skin surface. An ulcer forms under it. At the slightest injury to the inflamed area, the ulcer is opened and the separation of exudate begins. The oozing wound can be secondarily infected, which leads to purulent inflammatory processes.
Important:in this condition, complete wound healing is first required, and only after that a full-fledged surgical intervention is performed to remove the affected vessels.
Pulmonary embolism
An equally dangerous complication, in which a thrombus is detached from the inflamed vein and moves towards the pulmonary artery. This artery is directly involved in the organization of blood flow in a small circle, affecting the right ventricle of the heart. If the diameter of the detached thrombus is less than the lumen of the artery, then the clot moves to the branches of the pulmonary artery, provoking pulmonary edema or infarction. In this case, the patient will feel significant chest pain. A wet cough mixed with blood, an increase in body temperature, and weakness will also appear. If the diameter of the clot is equal to the diameter of the lumen of the pulmonary artery, then there is an instant blockage and death for the patient.
Detachment of a blood clot can be triggered by the following conditions:
- carrying out surgical interventions;
- oncology;
- heart failure;
- long bed rest.
Conservative and surgical treatment
Varicose veins can be treated both conservatively and operatively, depending on the stage of the pathology and the patient's condition. With conservative treatment, the administration of phlebotonic medications is indicated. Outwardly, gels and venotonic ointments based on horse chestnut are used. It should be understood that conservative treatment works only at the very initial stages of varicose veins.
As additional measures in the conservative treatment of varicose veins, physical activity (walking) and the wearing of compression hosiery are shown.
Minimally invasive and surgical methods of treatment
If the process of varicose veins and venous insufficiency has gone far, then they resort to minimally invasive or full-fledged surgical intervention in order to improve the patient's condition. Minimally invasive methods of intervention include the following:
- Sclerotherapy. In this case, a special sclerosing drug is injected into the lumen of the patient's varicose vein using a thin insulin needle. The injected substance first causes inflammation and then sclerosis of the diseased vein. The lumen of the diseased vessel is simply overgrown. The technique has rather a cosmetic effect, but does not solve the problem (cause) of the pathology itself. Relapses are possible after sclerotherapy. Contraindications to such an intervention are pregnancy, lactation and intolerance to the components of the drug.
- Stripping. Using this method, the diseased vein is removed using the thinnest probe. The peculiarity of surgery is that only the diseased part of the vessel can be removed, leaving its healthy parts. The operation is performed through two endoscopic punctures located on both sides of the site of the inflamed vessel. That is, scars and scars after such an intervention will not be visible.
- Microflebectomy. Removal of the diseased vein is also performed through several small incisions in the skin.
- Laser coagulation. Exposure to the lumen of a diseased vessel with a laser. As a result, the lumen of the vein is completely overgrown.
A full-fledged surgical intervention (abdominal operation) is called phlebectomy. With this method, the surgeon makes a complete incision of the skin of the leg in order to remove the entire superficial vein. The indications for such an operation are:
- a large volume of varicose veins;
- large cavity (lumen) of diseased vessels (more than 10 mm);
- thrombophlebitis;
- the presence of large varicose veins;
- the formation of trophic ulcers in the patient;
- lack of effectiveness of minimally invasive surgery.
Traditional methods of treatment
At the initial stages of pathology, you can also resort to folk methods of treating varicose veins. In particular, in combination with drug treatment, you can use the following folk remedies:
- The tomato is green. Thin slices of vegetable are placed on the area of inflamed veins and fixed with a bandage. You need to change such applications every 2-3 hours. The course of treatment is until a clear improvement in the condition.
- Potatoes. A bandage soaked in freshly squeezed potato juice is applied to the legs. Cover the top with cling film. Such applications are best done at night until the patient's condition improves.
- Apple cider vinegar. Preferably homemade. Vinegar is diluted in water (1 glass of water and 2-3 tablespoons of vinegar). A bandage is moistened in a solution and applied to the area of diseased veins. The bandage is fixed at night. You can also simply lubricate your feet with this solution at night. It is shown to take vinegar water and inside. Add 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar and a teaspoon of honey to a glass of water so as not to burn the esophagus with vinegar (the esophageal walls are very susceptible to acids). Drink the mixture in the morning on an empty stomach. The course of treatment with vinegar is 30 days.
- Horse chestnut. Flowers of the plant in the amount of 50 gr. pour 0. 5 liters of alcohol and insist for two weeks in a dark place, periodically shaking the mixture. The finished product is filtered through a mesh and drunk three times during the day, a tablespoon at a time. The mixture is washed down with water. The course of treatment is 7 days. Then a break of 14 days and again a seven-day course. Treatment according to this scheme is carried out until the infusion ends. Then it can be prepared again and the therapy regimen repeated.
- Burdock. In this case, fresh leaves of the plant are used to eliminate the disease. At night, sore feet are smeared with Vishnevsky's ointment and wrapped on top with a leaf of burdock. All are fixed with a bandage and put on compression hosiery. The bandage is worn for three days, and then it is removed and everything is washed off. It is possible to be treated in this way throughout the summer, while fresh burdock grows.
Important:such treatment is contraindicated in patients with high acidity of gastric juice.

conclusions
It is worth realizing that varicose veins are an irreversible pathology in most cases. Therefore, it is so important to take care of the health of your feet. Especially if there is a genetic predisposition to varicose veins. It is enough to give up bad habits, make your daily diet balanced, walk more and drink enough clean water a day. At the manifestation of the slightest signs of varicose veins, it is advisable to immediately contact a competent phlebologist to prevent complications of the disease. Remember, your health and the internal health of your feet is entirely up to you. And modern medicine and the hands of a professional can work wonders.























